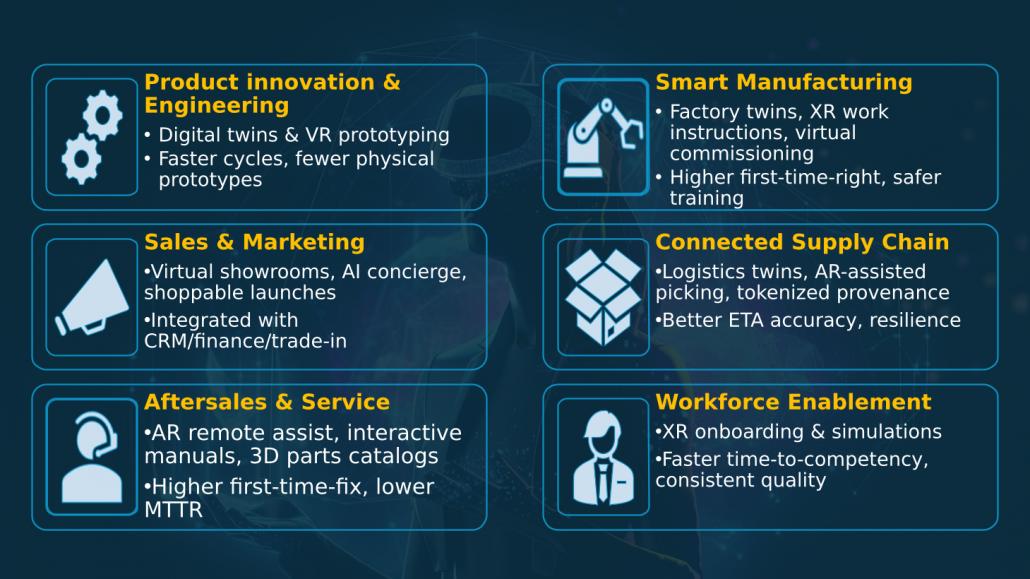
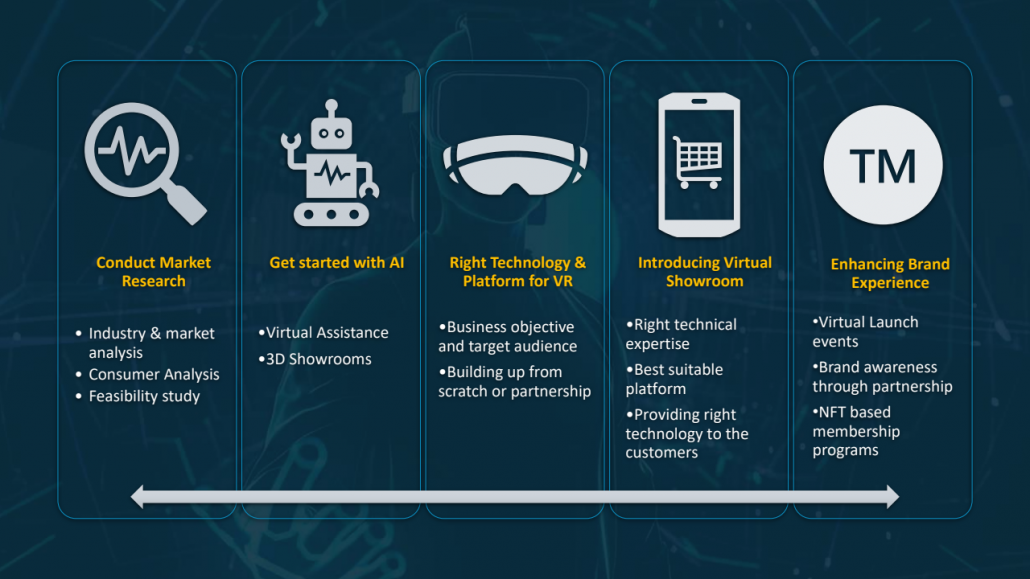
Introduction
The metaverse is a shared digital space that blends physical reality with virtual environments such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). It enables immersive settings for real-time interaction in work, social engagement, and commerce. In 2025, the metaverse is not a replacement for dealerships; it’s the immersive extension of omnichannel auto retail. When integrated with CRM and e-commerce flows (lead capture, financing, trade-in), metaverse touchpoints can lift sales productivity and conversion while reducing the need for incremental physical capacity.1
With AI accelerating across industries, the metaverse in the automotive industry is emerging as a key lever for future-ready automotive businesses. According to Persistence Market Research, the automotive market is valued at USD 4.38 billion in 2025 and projected to reach USD 30.6 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 32%.2 Although still in its early stages, adoption is growing as automakers explore new opportunities in design, sales, customer experience, and operations. From a sales and marketing perspective, the metaverse can revolutionize customer engagement through personalized experiences, global reach, community building, and data-driven insights.