Rethinking Legacy Analytics: AI-Driven Approaches to Modernizing SAS Workloads
Real-time analytics, cloud-native platforms, and machine learning are transforming the tech era at scale. Yet, many enterprises still depend on legacy Statistical Analysis Systems (SAS) for core data processing and reporting needs.
While SAS remains respected for its reliability and depth in statistical functions, the need to modernize towards open-source, distributed computing frameworks like PySpark (a component of Apache Spark) has become pressing.
This modernization is about replacing old tools with new ones and rethinking how legacy logic can be preserved and extended in a cloud-native world.
| 💡Did you know? More than 19,990 companies worldwide use Apache Spark, with PySpark as the Python-driven analytics and data engineering tool. Companies range from Fortune 1000 giants to mid-sized tech firms and startups.1 |
While the benefits are clear, the journey from SAS to PySpark is rarely straightforward. Migrating thousands of lines of legacy code, handling undocumented business rules, and bridging the gap between SAS’s batch procedures and PySpark’s distributed execution model present complex challenges beyond simple code translation.
In one of our modernization pilots, what began as a simple code migration uncovered over 1,200 undocumented SAS macros controlling core business logic. The real challenge wasn’t rewriting them. It was decoding years of institutional memory buried in syntax. That’s when we realized modernization is as much anthropology as it is engineering.
Read on to discover why these challenges matter, and how new AI-driven strategies can make modernization faster, safer, and more future-ready.
Understanding SAS and PySpark
Before planning any migration, it’s essential to understand what makes SAS and PySpark different, and why those differences matter for enterprise analytics.
SAS (Statistical Analysis System)
- Trusted tool offering analytics, business intelligence, and comprehensive data-management solutions.
- Remains strong in regulated sectors (healthcare, BFSI, government) due to its rigor and reliability.
- Proprietary licensing and single-node execution limit cost-effectiveness and scalability in the cloud era.
- Evolving data demands and modern workloads are pushing enterprises toward newer frameworks.
PySpark
- Built on Apache Spark’s in-memory engine, enabling scalable big-data processing and machine-learning in Python.
- Supports distributed computing across commodity clusters, offering flexibility, cost efficiency, and open-source adaptability.
- Integrates natively with cloud object stores (ADLS, S3, GCS) for seamless data access.
- Backed by a thriving open-source community, helping organizations accelerate innovation beyond closed ecosystems.
Why Modernize from SAS to PySpark?
Migrating to PySpark offers several significant advantages:
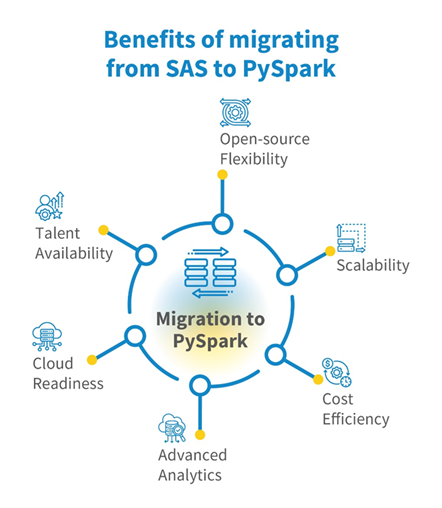
Figure 1: Key business and technical benefits of migrating analytics from SAS to PySpark
- Open-source flexibility: Customize pipelines and integrate community packages without license constraints. <what’s the business level impact?>
- Scalability: Effortlessly handle multi-terabyte datasets via Spark’s distributed engine.
- Cost efficiency: Lower infrastructure and license costs; autoscale clusters on-demand rather than maintaining costly SAS servers.
- Advanced analytics: Access to Spark MLlib, TensorFlow, and PyTorch for real-time or batch ML use cases.
- Cloud readiness: Native integration with Databricks
- Talent availability: Python and Spark skills are far more prevalent in the market, easing hiring and upskilling.
Challenges in SAS to PySpark Migration
Despite clear benefits, SAS-to-PySpark migration presents challenges:
- Legacy code complexity: SAS environments typically include complex, legacy codebases and intertwined dependencies that complicate migration.
- Varied coding practices: Diverse coding standards across teams complicate standardization and migration efforts.
- Functional and structural differences: Significant functional differences between SAS functions/macros and PySpark equivalents can lead to translation and performance discrepancies.
- Macro language nuances: SAS macro loops, global variables, and automatic variables (e.g., N) must be re-expressed in Spark idioms without losing business intent.
- Runtime behavioural gaps: Implicit pass-through SQL, PROC steps, and DATA step merge logic behave differently in Spark; careful testing is mandatory.
- Governance & validation: Enterprises must validate that migrated code yields byte-for-byte or business-rule-for-rule equivalent results to satisfy auditors.
AI-Driven Approaches: A Shift in Migration Thinking
Recent advances in AI, particularly through the Databricks Mosaic AI Agent Framework are transforming how enterprises modernize legacy analytics environments. Rather than relying solely on manual rewrites or static rule-based converters, Mosaic AI ecosystem allows for dynamic, content-aware migration powered by explainable, modular and auditable AI agents
However, AI alone isn’t enough. Effective modernization combines AI with structured, explainable workflows. A multi-stage process typically includes:
- Parsing and pre-processing: Breaking legacy code into smaller, logical units and identifying patterns, dependencies, and business rules.
- Context-aware translation: Using LLMs to generate PySpark code, guided by prompts designed to capture business semantics rather than surface syntax alone.
- Automated validation: Checking that generated code is structurally sound, aligns with expected schemas, and retains the intent of the original logic.
- Feedback loops: Iteratively refining translations when validation fails, making the process more reliable over time.
- Human oversight: Keeping domain experts in the loop to review critical transformations and validate edge cases.
This architecture mirrors best practices in software engineering: modular design, explainability, and continuous improvement.
A Closer Look: An Example of Structured AI-Driven Modernization Using Databricks
One example of this architectural approach is Scintilla.AI, developed by LTIMindtree. Scintilla.AI is an enterprise-grade, AI-driven platform that automates SAS-to-PySpark code migration within Databricks environments with up to 80% accuracy.
It ensures contextual understanding, data lineage tracing, and domain-driven validation for transparent, efficient, and optimized migrations. Rather than offering a black-box converter, Scintilla.AI uses an agent-based pipeline:
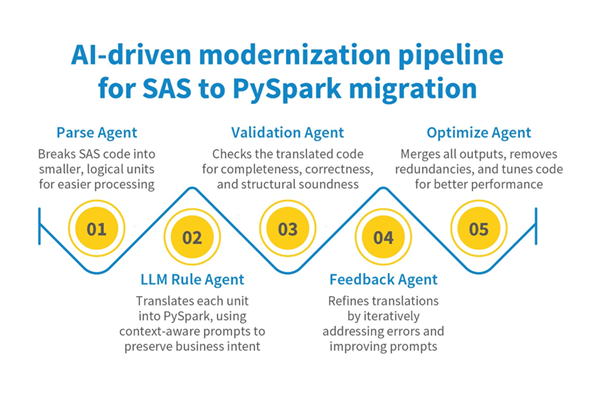
Figure 2: Stages of the Scintilla.AI agent-based pipeline for safe and transparent SAS-to-PySpark migration
- A Parse agent breaks SAS code into manageable segments and creates an intermediate representation.
- An LLM Rule agent translates those segments into PySpark, guided by carefully engineered prompts.
- A Validation agent automatically checks for completeness, correctness, and structural integrity.
- A Feedback agent retries translation when errors are found, refining prompts as needed.
- A Optimize Agent merges the output code and enhances code performance and efficiency, reducing redundancies and improving execution.
This layered design allows migration to be transparent, testable, and iterative. It also means that domain experts can see how legacy business rules are preserved, review intermediate outputs, and document transformation decisions, which are critical in industries with strict compliance requirements.
Importantly, such an approach is adaptable. While the current focus might be SAS-to-PySpark, the same principles could extend to other legacy-to-modern migrations, like PL/SQL to Spark SQL or COBOL to modern data frameworks.
Why This Matters Now
Modern data strategies demand more than just cost savings. They require agility: the ability to experiment with machine learning, to scale up processing for new data sources, and to deliver insights faster.
AI-driven modernization approaches offer:
- Reduced risk: Automation lowers human error while validation ensures correctness.
- Preservation of knowledge: Intelligent parsing and translation retain critical business logic.
- Speed: Large codebases can be processed faster, making modernization projects feasible.
- Explainability: Logs, intermediate artifacts, and dashboards give teams confidence in what was changed, and why.
Enterprises can move forward without fear of losing institutional knowledge by turning migration from a single high-risk rewrite into a transparent, incremental process.
Conclusion
Modernizing SAS workloads to PySpark is a technical upgrade and an opportunity to realign data infrastructure with cloud-native, AI-driven analytics demands. While the challenges are real, complex legacy code, business-critical logic, and governance requirements, new AI-driven approaches show that modernization can be both explainable and scalable.
Architectures that combine parsing, large language models, validation, and iterative feedback create a blueprint for safer, faster migration, bridging the gap between legacy systems and the promise of modern data platforms.
In doing so, they help organizations preserve what matters most: the business knowledge built into decades of analytics while unlocking the speed and flexibility required for what’s next.
References
1Companies using Apache Spark, enlyft: https://enlyft.com/tech/products/apache-spark
2AI Agents: Mastering Agentic RAG – Part 5, Shivam Goyal, Microsoft: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/blog/educatordeveloperblog/ai-agents-mastering-agentic-rag—part-5/4396171
3Fully managed Retrieval Augmented Generation options on AWS, AWS Documentation: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/prescriptive-guidance/latest/retrieval-augmented-generation-options/rag-fully-managed.html
More from Ramesh Vanteru
Enterprises worldwide are emphasizing flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness to stay…
Modern-day organizations that generate a huge amount of data look forward to leveraging the…
In the ever-evolving data processing landscape, transitioning from traditional systems to modern…
Latest Blogs
A closer look at Kimi K2 Thinking, an open agentic model that pushes autonomy, security, and…
We live in an era where data drives every strategic shift, fuels every decision, and informs…
The Evolution of Third-Party Risk: When Trust Meets Technology Not long ago, third-party risk…
Today, media and entertainment are changing quickly. The combination of artificial intelligence,…




